Fire occurs whenever combustible fuel in the presence of oxygen at an extremely high temperature becomes gas. Flames are the visual indicator of the heated gas. Fire can also occur from lower-temperature sources. Over time, combustible materials such as smoldering embers can reach their ignition temperature.
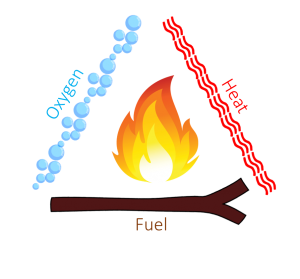
The fire triangle is a simple way of understanding the elements of fire. The sides of the triangle represent the interdependent ingredients needed for fire: heat, fuel and oxygen.

A heat source is responsible for the initial ignition of fire, and is also needed to maintain a fire. Heat allows fire to continue even with damp fuel by drying it out and preheating it.

Fuel is any kind of combustible material. It’s characterised by its moisture content, size, shape, quantity and the arrangement on the fire. The moisture content often determines how easily it will burn.

Air contains about 21 percent oxygen, most fires require at least 16 percent oxygen to burn. Oxygen supports the chemical process that occurs during a fire. When fuel burns, it reacts with oxygen from the surrounding air, releasing heat and generating combustion products (gases, smoke, embers, etc.). This process is known as oxidation.

